What is MATCH?
The Monitoring and Tracking Chemicals (MATCH) project is a prototype software platform designed to test the feasibility of blockchain technology as a tool to reconcile discrepancies in the international transfer of dual-use chemicals covered under Schedule 2 and Schedule 3 of the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC). MATCH utilizes distributed ledger technology (DLT), commonly referred to as blockchain technology, to record transactions of dual-use chemicals as they are traded between fictional CWC States Parties who must also declare these transfers annually to a “World Authority.” MATCH’s hypothetical ecosystem simulates global chemical trade and regulatory reporting using real-world trade data and national CWC implementing legislation and streamlines the way international chemical transfers are recorded and declared between chemical industry entities and national CWC authorities.
The MATCH Ecosystem
The MATCH ecosystem is comprised of three types of stakeholders, or participants: “entities,” “national authorities,” and a “World Authority.”
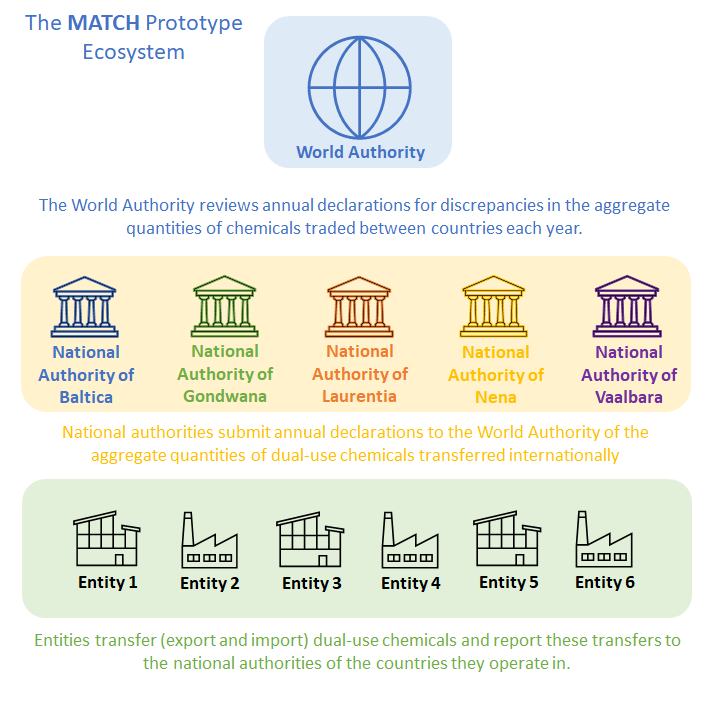
Entities broadly represent the global chemical industry. MATCH’s six entities share information on the export and import of chemicals traded between them and report the quantities of chemicals traded annually or semi-annually to their respective national authorities.
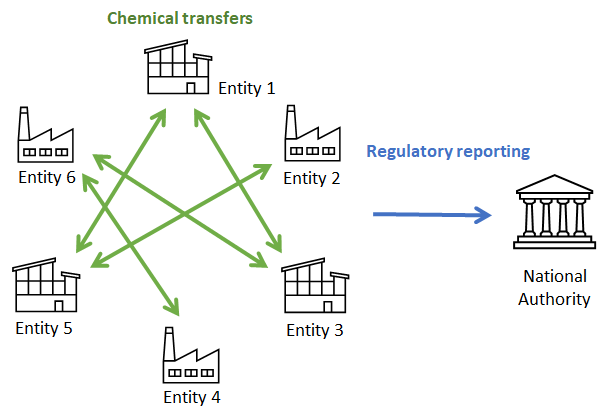
National Authorities represent the governmental authorities responsible for implementing the CWC in each State Party. MATCH has five fictional CWC States Parties, Baltica, Gondwana, Laurentia, Nena, and Vaalbara, each with a corresponding national authority. Entities submit reports to the national authority of the country in which quantities of chemicals were exported or imported. National authorities then make an annual declaration to the World Authority of the aggregate quantities of each Schedule 2 or Schedule 3 chemical transferred by entities in their country.
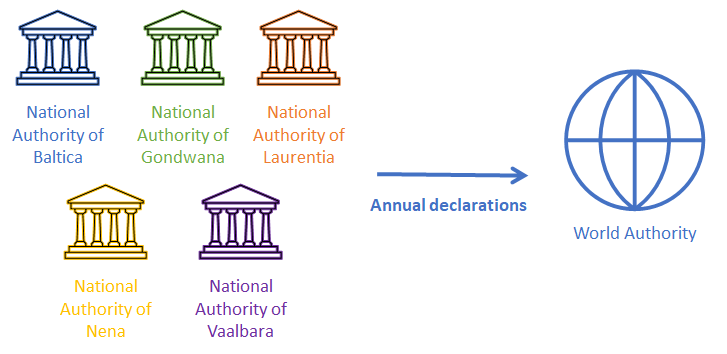
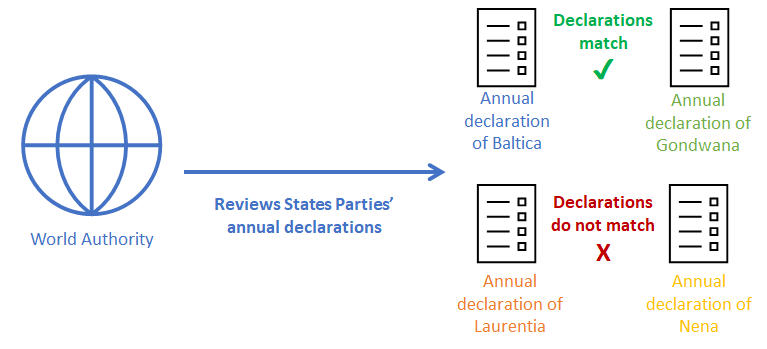
The World Authority collects annual declarations on past transfers of scheduled chemicals from MATCH’s five national authorities and reviews them for discrepancies in the aggregate quantities of chemicals traded between countries each year.
Dual-use Chemicals: The MATCH prototype allows entities to report transfers (exports and imports) of four dual-use chemicals that are controlled, or “scheduled,” under the CWC. Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA), triethanolamine (TEA), and phosphorus trichloride fall under Schedule 3, and Amgard 1045 (CAS RN 42595-45-9) falls under Schedule 2B.
Tracking Chemical Transfers
In MATCH, entities create export and import records to share key information on the dual-use chemicals they trade with their foreign trade partners, such as the chemical’s Schedule under the CWC, IUPAC chemical name, CAS Registry number, associated Harmonized System Code, and the quantity and concentration (purity) of scheduled chemical in each transfer.
Importing entities receive automatic notifications of pending exports which contain a QR code from which the importer may create an import form automatically populated with data from the export record. MATCH also alerts both trade partners of any discrepancies that arise in the quantities of chemicals recorded by the exporter and importer. This feature potentially allows exporters and importers to identify and resolve discrepancies in their trade records before they are reported to national authorities.
Automating Industry & State Party Declarations
MATCH enables entities to report international transfers of dual-use chemicals to the national authorities of the countries they operate in. The entity selects a reporting period from which quantities of all its past exports and imports are automatically populated into a report form. This report includes both the aggregate quantities of the chemicals transferred and a list of the countries the reporting entity has exported to or imported from.
When National authorities create their annual declaration to the World Authority using MATCH, data on transfers to and from that country is automatically aggregated based on quantities reported by entities during that year. Each declaration form includes a list of both the aggregate quantities of each Schedule 2 and Schedule 3 chemical transferred internationally and the countries each chemical was exported to or imported from.
Once these declarations are submitted to the World Authority, MATCH automatically detects discrepancies in the quantities of transferred chemicals declared by each State Party. If the quantities of exported and imported chemicals declared by two national authorities do not match, MATCH will alert the World Authority.
A Novel Solution to Streamline Declarations & Resolve Discrepancies
MATCH processes each chemical transfer, report to a national authority, and declaration to the World Authority instantly, and automatically cross-references and checks entity transfer records and national authority declarations for discrepancies. This in turn significantly reduces the occurrence of common discrepancies, such as typos and calculation errors, and provides industry and national authorities with increased provenance over the history of past transactions.
Additionally, each time MATCH processes a transaction, the prototype’s underlying blockchain technology ensures both data security and immutability. MATCH creates a blockchain certification for each transaction containing a unique key, known as a “hash,” which is stored on a permissioned blockchain network. Each hash is combined with other hashes to form “blocks” of encrypted data that are replicated among the distributed nodes of the network. Any attempt to alter a hash or its corresponding certification is instantly detected and rejected by the system. Blockchain technology also allows MATCH to enforce strict permissions limiting the access of each participant, ensuring that entities, national authorities, and the World Authority only have access to their own data and information willingly shared by other participants.
MATCH is being developed in partnership with Canada-based DLT developer OARO, with financial contribution by Global Affairs Canada’s Weapons Threat Reduction Program. The project began in September 2021 and will conclude in May 2023.
Want to Learn More About MATCH?
- Check out the MATCH Project webpage
- Watch the MATCH Animated Video
- Discover more about the causes of Transfer Discrepancies in Trade Flows of CWC Scheduled Chemicals
- Interested in the application of blockchain technology for international security? Check out our book!




